What Is Good Server Response Time?
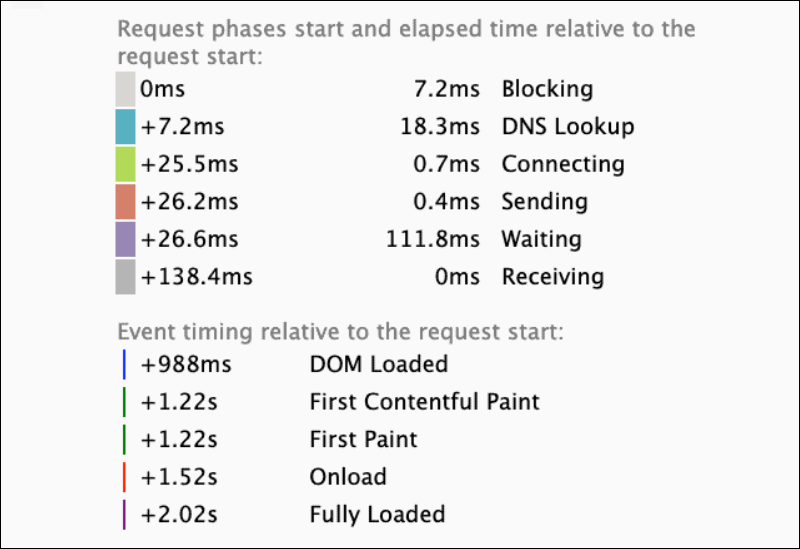
Google recommends you aim for a response time lower than 200 milliseconds. A 100ms TTFB is ideal, and everything over 500ms is an issue. This time must be consistent for all users. It should not vary depending on the users’ geographical positions.
Google classifies websites into three groups based on the speed score they achieve:
Fast (90-100)
Average (50-89)
Slow (0-49)
How to Improve Server Response Time
Here are seven easy ways to reduce the server response time for your website.
1. Use Reliable and Fast Web Hosting
Choosing free or low-cost web hosting might save money in the short term, but the tradeoff often includes sharing server resources with other tenants, limited technical support, and slower website performance.
A financially stable provider is more likely to invest in hardware, security, and innovative solutions.
To ensure optimal website performance, particularly in terms of load speeds and availability, look for the following when selecting a web hosting service:
Data Center Location. Select a provider with data centers near your target audience to enhance server response time and speed.
Bandwidth and Throughput. Verify that the host has the necessary capacity to support your website’s data demands, especially for data-intensive platforms.
Scalability. Commercial websites, for example, ecommerce stores, often experience traffic surges during holidays or due to trending products. The web host must be equipped to scale up server resources and guarantee uninterrupted service and speeds during peak times.
Customer Support Services. Look for 24/7 technical support to promptly address and resolve technical issues and ensure optimal website performance.
Cloud hosting is well-suited for businesses looking to enhance website load speeds without significant upfront investments. Companies with consistent, predictable cloud workloads can reserve capacity in advance and benefit from discounted rates.
2. Use a CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) distributes website content across a global network of proxy servers. When a user visits a website, the CDN redirects their request to the nearest server in this network.
Users receive cached HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos from the closest server. The proximity reduces latency, the time it takes data to travel between the user and the server, and results in faster website loading times.

CDN providers offer advanced DNS management services like enhanced security, improved website performance tools, and uptime guarantees. These features and benefits are crucial for maintaining a robust online presence, especially for websites with high traffic or a global audience.
Notable CDN/DNS providers include Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront (part of AWS services), and Google Cloud CDN.
3. Optimize Databases
As databases grow over time, they become less efficient at storing and accessing data. To improve database performance, you need to remove unnecessary data, reduce the size of the database, and optimize its structure. The faster the database completes its operations, the faster the server responds to the website visitor's request.
Database optimization strategies vary based on the database type and database management tools. Web hosts often provide access to direct management interfaces like phpMyAdmin or cPanel by default. These tools enable clients to manage and optimize their databases within a graphical and user-friendly environment. Advanced users can create custom scripts to automate and schedule optimization tasks.
WordPress website owners can also use cPanel or phpMyAdmin to manage their database. However, you can also install WordPress database optimization plugins. These plugins are specifically created to enhance WordPress database performance and can help you streamline the following operations:
Deleting unnecessary data such as post revisions and spam comments.
Compacting and defragmenting database tables.
Clearing out the trash folder.
Automating database clean-ups.
Database optimization plugins in WordPress also offer additional features such as data compression and caching, increasing the speed at which data is provided to the end user.
4. File Compression
Websites are no longer a collection of static pages but a dynamic platform with multiple datatypes and integrated third-party functionalities and features. The size of files being delivered to users is increasing, consequently prolonging TTFB.
File compression is a sound strategy for speeding up content delivery times. Gzip is a compression algorithm that can be implemented on web servers. It balances compression and speed and effectively compresses HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Another compression tool, Brotli, is a good choice for text-based content, even though its adoption is less widespread than Gzip's.
Gzip and Brotli can be integrated into a WordPress website through web server configurations or WordPress caching and optimization plugins. Such plugins enable users to implement these algorithms without modifying server settings directly.
5. Monitor PHP Usage
PHP scripts that are part of multiple concurrent server processes can contribute to higher resource usage, potentially slowing down the server's ability to serve a page to a visitor.
If you are running a PHP script, ensure it is not overtaxing vital CPU and memory resources. Avoid unnecessary database queries and implement caching strategies to reduce load times.
Outdated PHP versions are a significant security risk. Some hosting companies do not automatically update PHP, so this process often needs to be done manually.
You can check your PHP version using the command line or PHP code. If you have a WordPress website, verify the version using the PHP Compatibility Checker plugin.
Upgrade to a newer PHP version through cPanel or by contacting your hosting provider.
6. Configure Caching
While browsing a website, visitors often make identical or similar requests to the server. You can cache frequently requested data and server responses. The server delivers the stored (cached) content instead of processing the exact requests repeatedly.
Several caching strategies help you reduce server loads and speed up content delivery:
Caching database queries. Executing database queries is a resource-intensive task. Reduce the number of queries by storing results from frequent or repeated requests.
Web page caching. Save copies of fully rendered web pages in the cache. Servers can deliver these pages without additional processing.
Browser caching. Instruct browsers to store certain files locally on the user's device.
Pre-Caching. Analyze user behavior and anticipate subsequent requests. You can pre-load assets that are most likely to be needed for future interactions.
Object Caching. Cache the results of complex calculations and API call responses. Scripts do not need to process the same requests again or make additional API calls.